Functions
Functions are autonomous tools for specific tasks, guided by your base prompt.
graph LR
A([Start]) --> B[User Query]
B --> C[AI Receives Query]
C --> D{Check Prompt & Functions}
D -->|No Function| E[Direct Response]
D -->|Need Function| F[Function Handling]
subgraph Function Calls
F -.-> G[Function 1]
F -.-> H[Function 2]
F -.-> I[Function 3]
F -.-> J[Function N]
end
G & H & I & J -.-> K[Collect Results]
K --> L[Generate Response]
E --> L
L --> M[Send to User]
M --> N([End])
%% Layout adjustments
A --- C
J --- N
classDef default fill:#f0f4f8,stroke:#506480,stroke-width:2px;
classDef process fill:#d0e3ff,stroke:#3474eb,stroke-width:2px;
classDef decision fill:#ffeeba,stroke:#d39e00,stroke-width:2px;
classDef start_end fill:#d4edda,stroke:#28a745,stroke-width:2px;
classDef function fill:#e8d8ff,stroke:#6f42c1,stroke-width:2px;
class A,N start_end;
class B,C,E,K,L,M process;
class D decision;
class F,G,H,I,J function;
Functions act as tools or micro-agents that perform specific tasks. They are autonomous and can be guided using your base prompt.
Benefits
-
Chained Execution: AI can execute a chain of functions to answer complex queries. For example, for the query "weather of India & current time," the AI would first call a function to get the weather in India and then another function to get the current time in India.
-
Easy Setup: Functions are simple to set up. You only need to enable the function and, if needed, guide when the function should execute by defining it in your base prompt settings. For example, "Use Websearch function to answer any stock price-related questions and do not use web search for any other purpose."
Cons
-
Sequence Limitations: Long sequences that require input across multiple messages may not work effectively.
-
Customization Constraints: There are limitations on how much you can customize the functions.
Getting Started
Navigate to Functions
From your YourGPT dashboard, navigate to Automation > Functions in the left sidebar. You'll see four types of functions available:
- System Functions - Pre-built system function templates
- Code Functions - Custom code execution functions
- API Functions - External API integrations
- MCP Servers - Model Context Protocol servers to enable your YourGPT AI Agent to call external tools and services.
System Functions
Select System Functions from the dropdown menu to access pre-built function templates. Click the Add System Function button to enable:
- Web Search: This function performs web searches to fetch real-time information from the web, such as the latest news, weather updates, or stock prices.
Code Functions
Code Functions allow you to create custom code execution functions using JavaScript or Python. These functions enable your AI to perform complex operations, data processing, or integrate with services through code.
Navigate to Code Functions
Select Code Functions from the dropdown menu and click the Add New Function button.
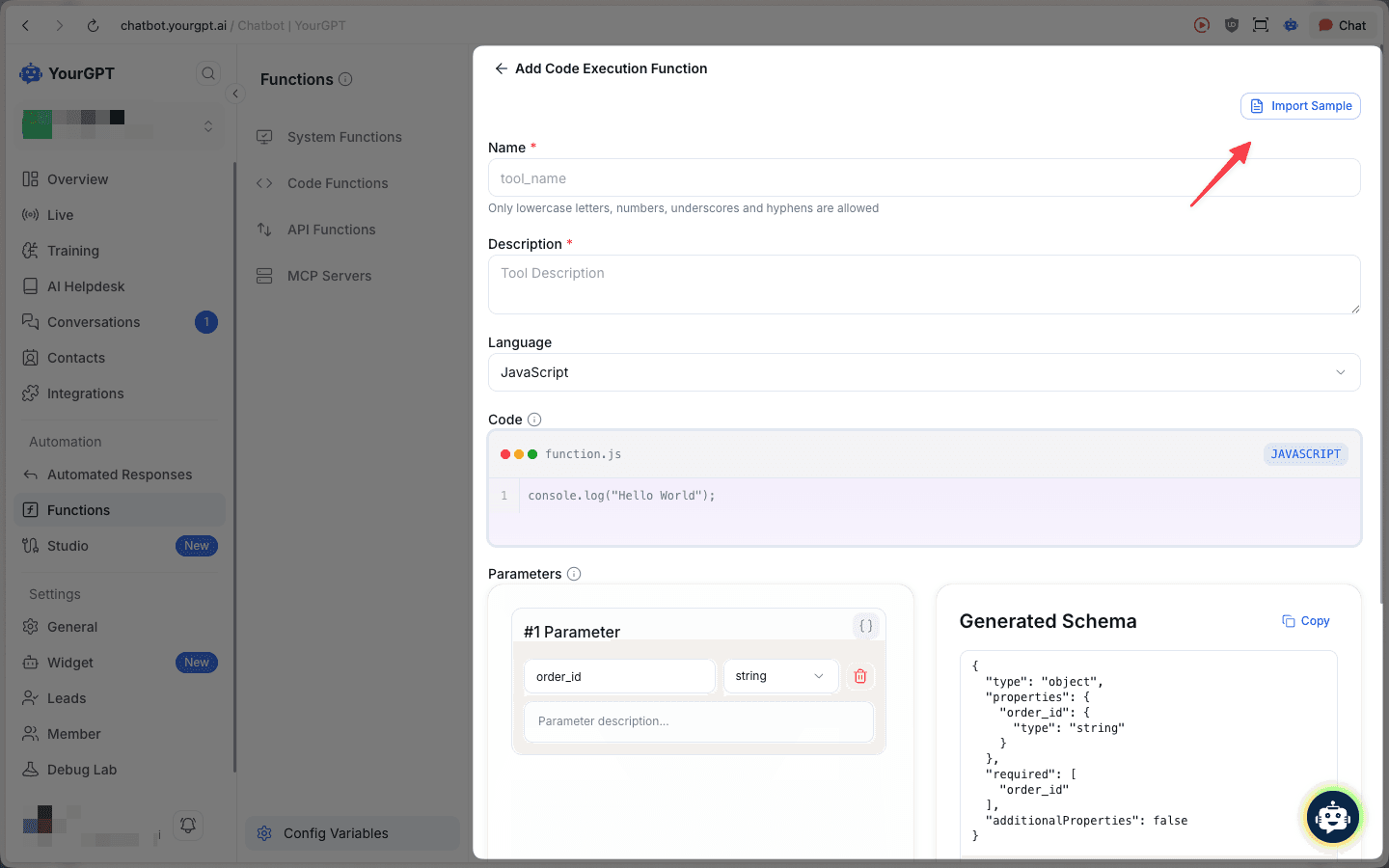
Configure Function Details
Fill in the basic information for your code function:
- Name: Enter a function name using only lowercase letters, numbers, underscores, and hyphens (e.g.,
create_post,update_todo) - Description: Provide a clear description of what the function does
- Language: Select either JavaScript or Python
- Code: Write your custom code in the syntax-highlighted editor
Define Parameters
Add parameters that your function needs to execute:
- Click Add Parameter to create a new parameter
- For each parameter, specify:
- Parameter name: The variable name (e.g.,
title,body,order_id) - Type: Select from string, number, boolean, etc.
- Description: Explain what this parameter is for
- Parameter name: The variable name (e.g.,
The Generated Schema panel on the right automatically updates as you add parameters, showing the JSON schema in real-time.
Tip: You can edit the JSON schema directly and click "Apply Changes" to update the parameter builder. Parameters use JSON Schema format for validation and are always required in strict mode.
Import Sample Code (Optional)
Click the Import Sample button to load pre-built examples:
- Create Blog Posts: HTTP POST request to create blog posts with title and body parameters
- Update Todo Items: PATCH request to update todo items with dynamic URLs and status management
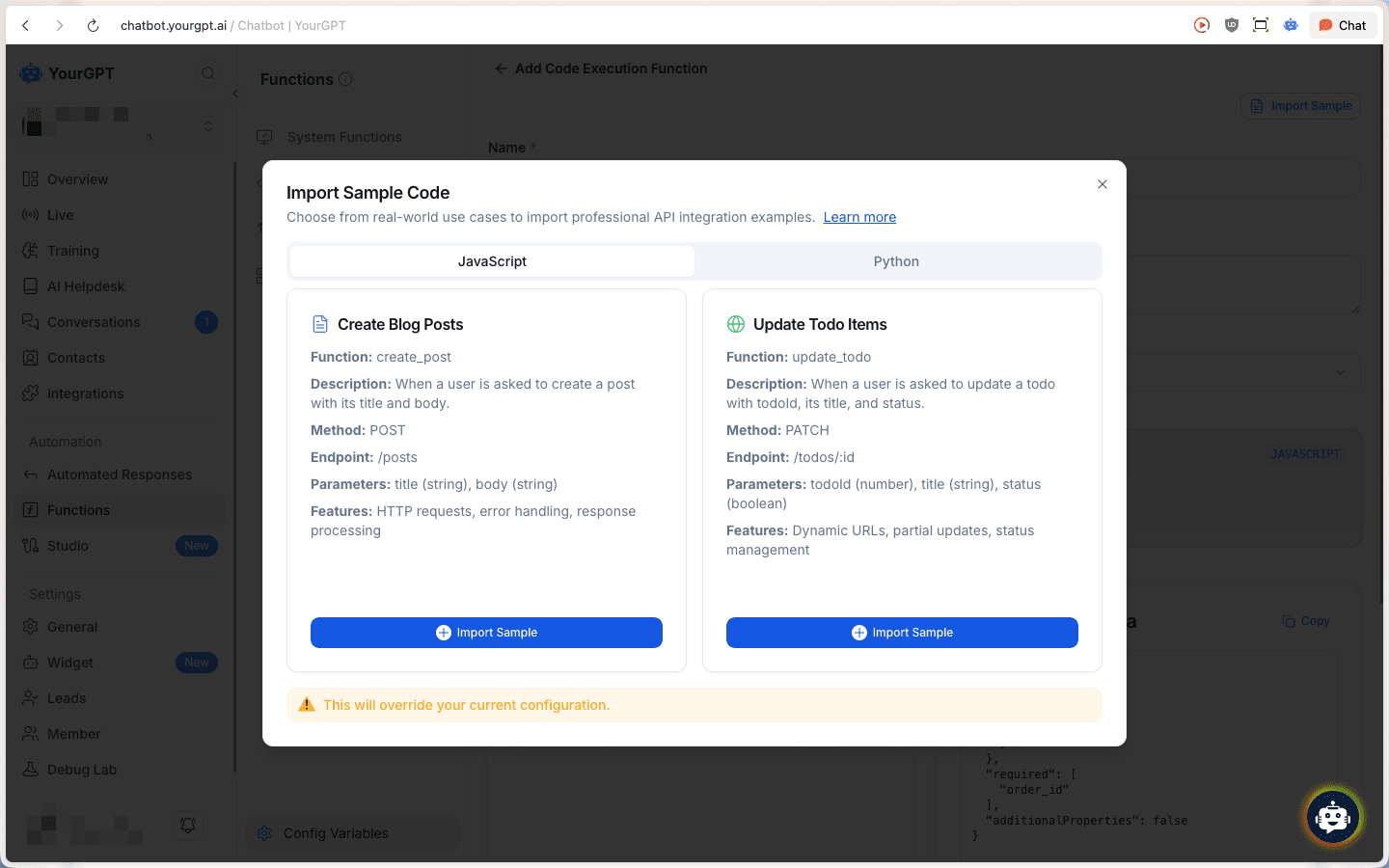
Importing a sample will override your current configuration.
Review and Save
Review your function configuration, including all parameters and the generated schema. The code editor shows your complete function with line numbers and syntax highlighting.
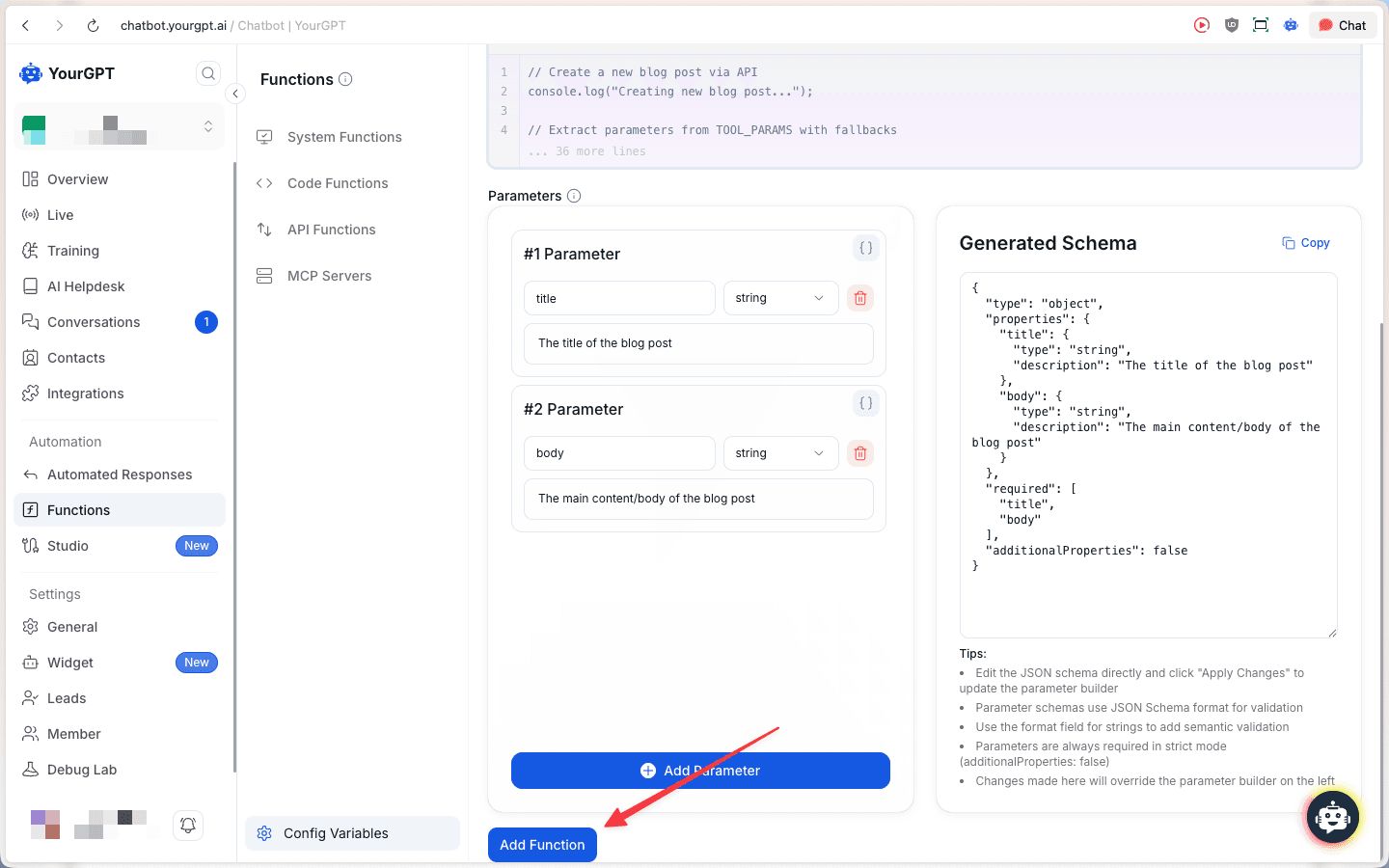
Click Add Function to save your code function.
API Functions
API Functions allow you to connect your AI to external APIs and integrate their data or services into your chatbot responses. You can call any REST API and define how your AI should interact with it.
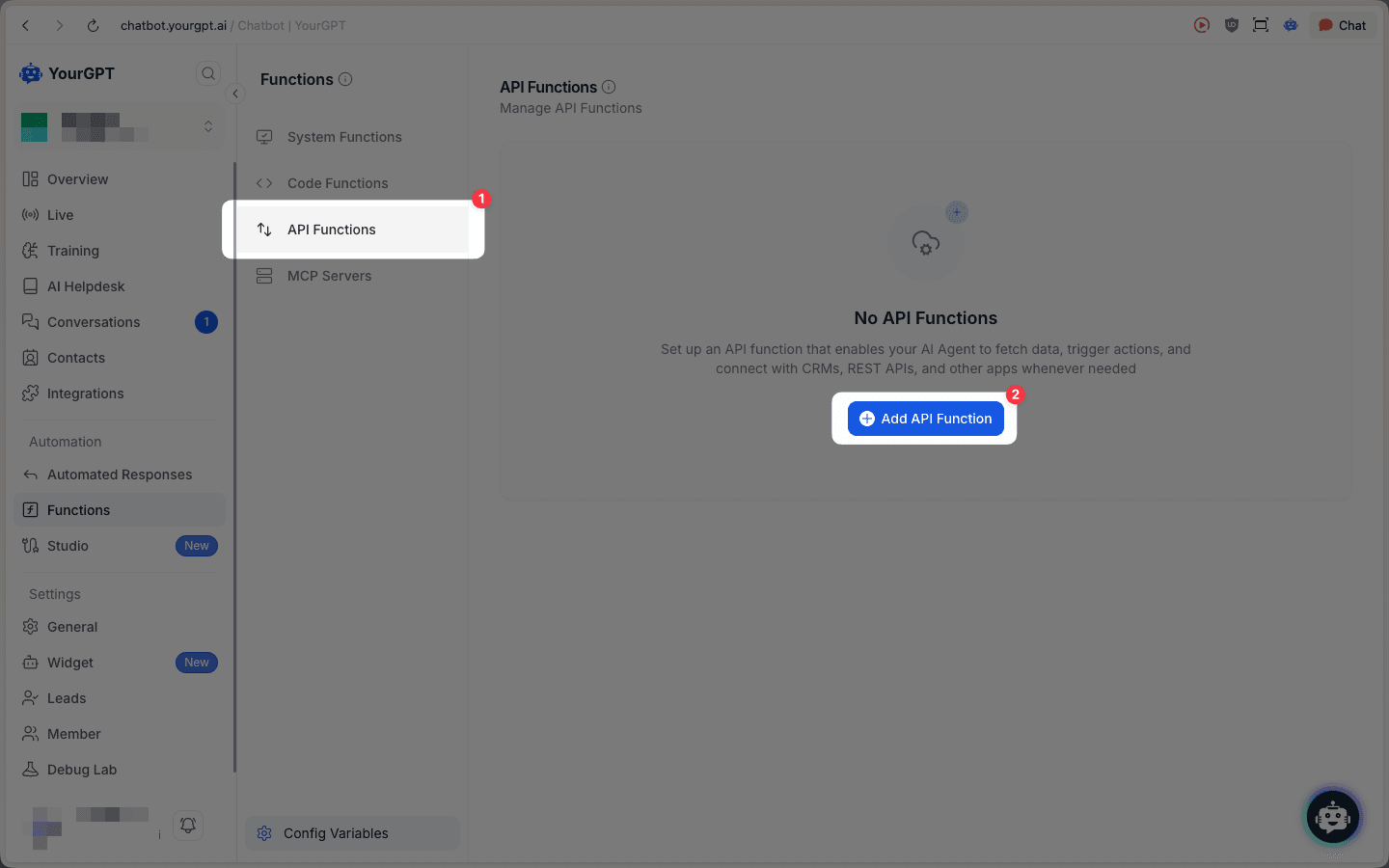
Navigate to API Functions
Select API Functions from the dropdown menu and click the Add API Function button.
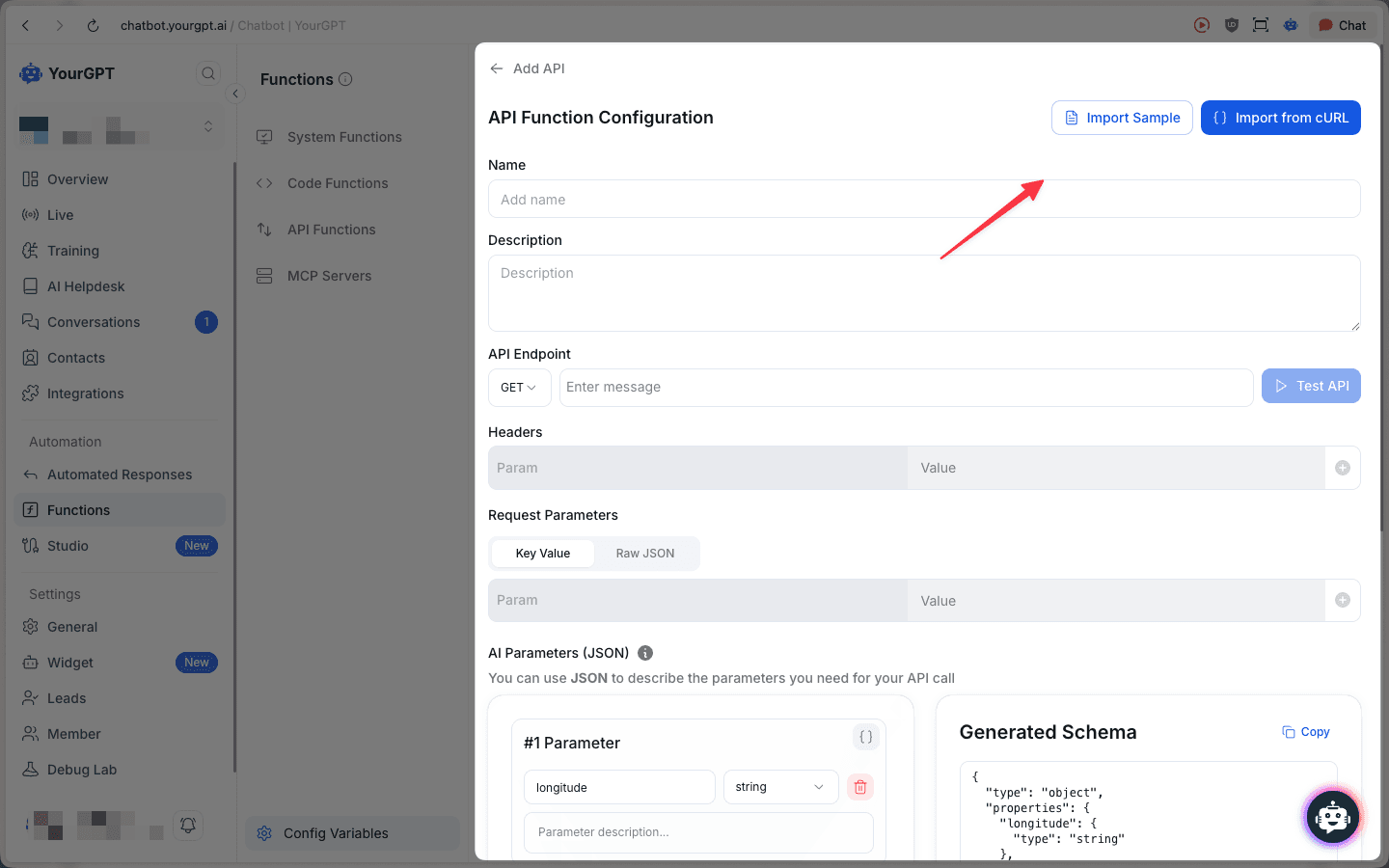
Configure API Details
Fill in the basic information for your API function:
- Name: Enter a descriptive name for your API function
- Description: Provide a brief explanation of what the function does
- API Endpoint:
- Select the HTTP method (GET, POST, PATCH, PUT, DELETE, etc.)
- Enter the endpoint URL for the API you want to call
- Click Test API to verify the endpoint works
Add Headers and Request Parameters
Configure the API request details:
Headers: Add any necessary headers required by the API (e.g., Authorization, Content-Type). Click the + button to add more headers.
Request Parameters: Add query parameters or request body data:
- Key Value tab: Add parameters as key-value pairs
- Raw JSON tab: Enter parameters as raw JSON
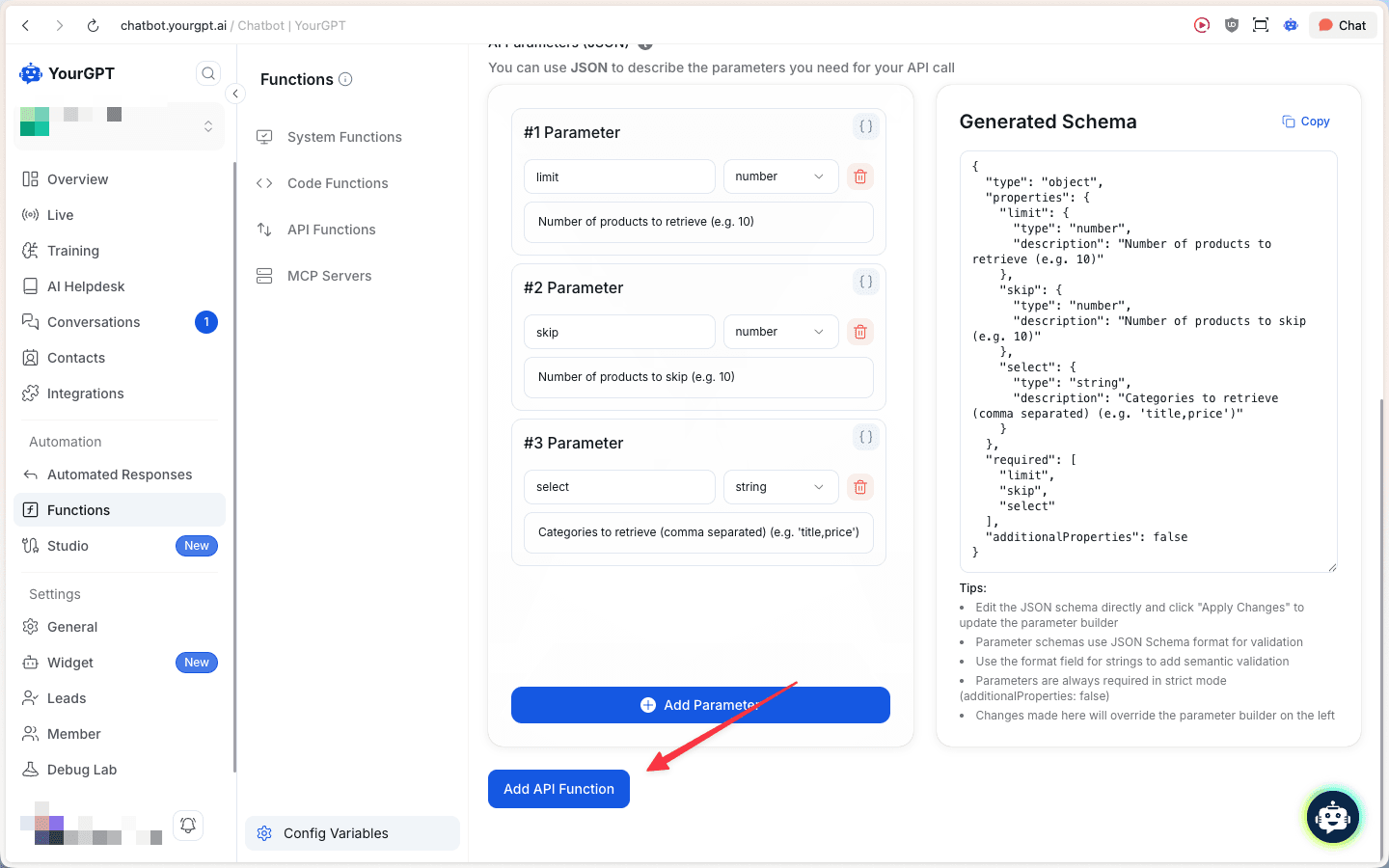
AI Parameters (JSON): Define the parameters that the AI needs to collect from the user to call the API. For each parameter, specify:
- Parameter name: The variable name (e.g.,
limit,skip,select) - Type: Select from string, number, boolean, etc.
- Description: Explain what this parameter is for
The Generated Schema panel shows the auto-generated JSON schema based on your parameters.
Tip: You can edit the JSON schema directly and click "Apply Changes" to update the parameter builder. Use the format field for strings to add semantic validation.
Import Sample API (Optional)
Click the Import Sample button to load pre-configured API examples:
- Products API: GET request to fetch products with limit, skip, and select parameters
- Recipe API: Additional sample API configurations
Alternatively, use Import from cURL to convert cURL commands directly into function configuration.
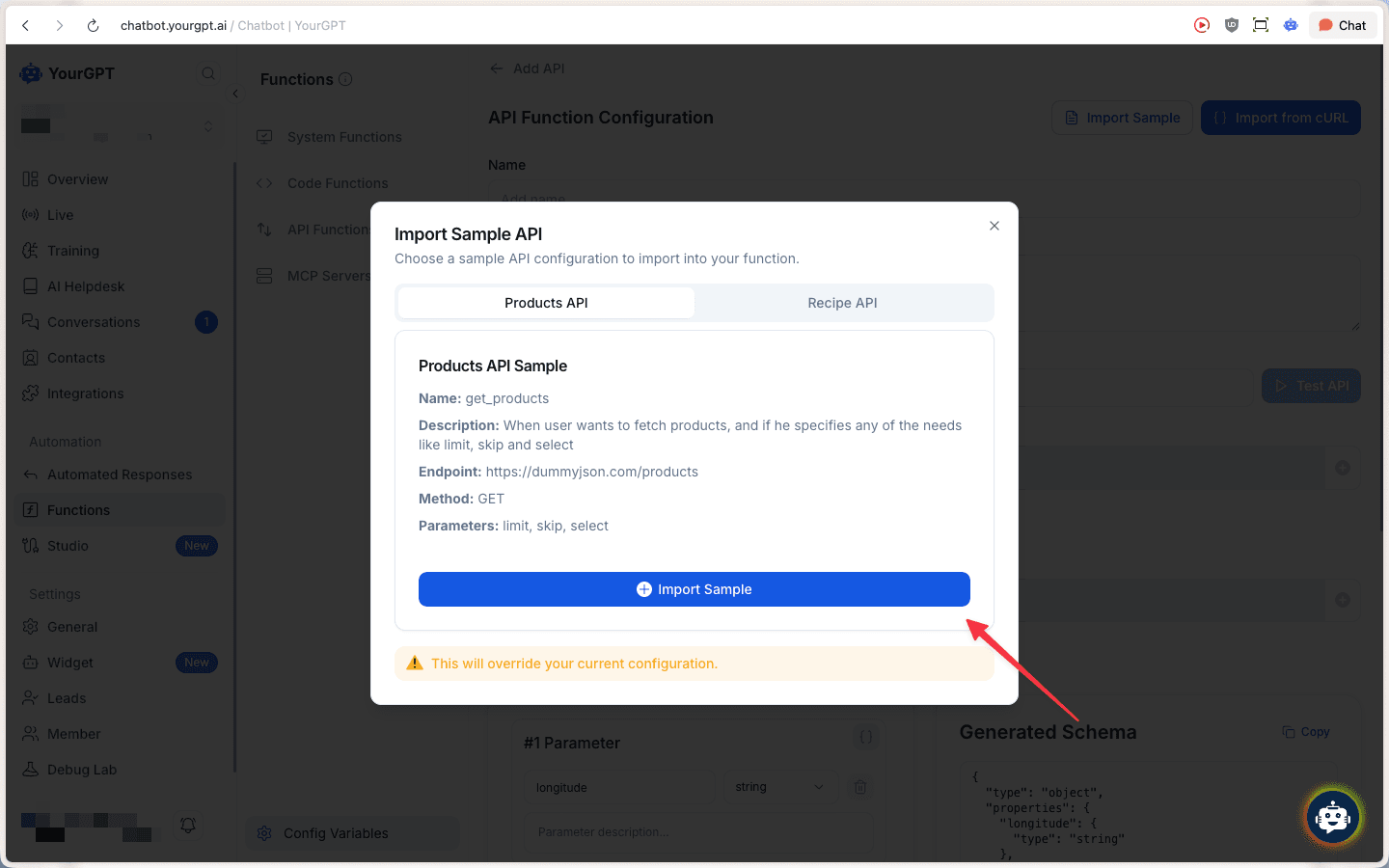
Importing a sample will override your current configuration.
Review and Save
Review your complete API function configuration, including all parameters and the generated schema. Verify that:
- All required parameters are defined
- The API endpoint is correct
- Headers are properly configured
Click Add API Function to save your configuration.
Examples
Weather API
If you want to add a function that retrieves weather information based on geographic coordinates, you might set it up as follows:
- Name: Get Weather
- Description: Retrieves the current weather information based on longitude and latitude.
- API Endpoint:
GEThttps://api.weather.com/v3/wx/conditions/current - Headers:
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY - Parameters (JSON):
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"longitude": {
"type": "string"
},
"latitude": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": ["longitude", "latitude"]
}Function Usage:
- Once the function is added, your chatbot can access the weather API and retrieve relevant weather information based on the user's query.
- Users can trigger the function by using a specific keyword or phrase like "what's the weather like in [location]". The chatbot will then use the location to determine the latitude and longitude, which are passed as parameters to the function.
Find Flight API
Let's say you want to create a function to find the cheapest flight for a given destination from a specific origin.
Function Setup:
- Name:
cheapest_flight_api - Description:
API to find the cheapest flight from origin to destination - API Endpoint:
https://your_flight_api.com/cheapest
Parameters Definition:
The function accepts two parameters, origin and destination, both of which are strings representing the departure and arrival airports respectively.
Parameters (JSON):
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"origin": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The departure airport."
},
"destination": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The arrival airport."
}
},
"required": ["origin", "destination"]
}Function Usage:
- Once the function is added, your chatbot can access the flight search API and retrieve relevant results based on the user's query.
- The chatbot can execute the function when a user inputs a phrase like "find cheapest flights from [origin] to [destination]", The chatbot can then display the cheapest flight options to the user, including details such as flight numbers, departure and arrival times, and prices.
Useful Links
Additional Resources
For more detailed guides on setting up functions with tool parameters, check out these helpful articles:
MCP Functions
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that enables your AI agent to securely connect with tools. By using MCP servers, you can give your agent capabilities like accessing local data, google maps, keywords tools, or any other tools.
Why Use MCP?
- Standardization: Use a common protocol to connect any tool or data source.
- Security: Run servers locally or securely on your infrastructure.
- Flexibility: Connect to anything from identifying local files to complex enterprise systems.
To get started with MCP, navigate to Functions > MCP Servers and add the MCP server details to connect your first server.